Properties of
solution that depend on the ratio of no: of solute particles to the total no:
of particles in the solution.
1. Relative lowering of
vapour pressure:
⇒ Vapour
pressure of solvent in solution is less than that of pure solvent.
According to
Raoult’s law
PA = XA
x P°A
⇒ So the
reduction in vapour pressure is given as
Δ PA =
P°A - PA
i.e., Δ PA
= P°A (1 - XA) = P°AXB

i.e., therefore, relative lowering of vapour pressure ΔPA/PA is equal to mole fraction of solute XB.

i.e., therefore, relative lowering of vapour pressure ΔPA/PA is equal to mole fraction of solute XB.
⇒ If two or
more non-volatile solutes are present then it is equal to sum of the mole
fraction of the solutes




For dilute solution:

Where, wA = mass of solvent
MA =
Molar mass of solvent
WB =
mass of solute
MB =
Molar mass of solute
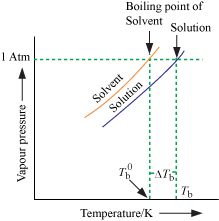
2. Elevation of boiling
point:
⇒ A liquid boils
at a temperature where its vapour pressure becomes equal to atmospheric
pressure.
⇒ Since in a
solution the vapour pressure of solvent is reduced, the temperature needs to be
raised to increase the vapour pressure to atmospheric pressure.
⇒ Therefore, the
boiling point of solution is always higher than that of pure solvent.
ΔTb =
Tb - T°b
= elevation in boiling point
Tb=
boiling point of solution
Tb0
= boiling point of pure solvent

For dilute solution:
Tb α m
Δ Tb =
Kb x m
m = molality
Kb =
molal elevation constant (Ebullioscopic Constant). Units: K kg mol-1


R = gas constant
M1 =
molar mass of solvent
ΔvapH =
enthalpy of vaporization
3. Depression of freezing
point:
⇒ A solution
freezes when its vapour pressure becomes equal to the vapour pressure of pure
solid solvent.
⇒ As the
vapour pressure of a solvent decreases when a non-volatile solute is added, the
freezing point of solvent decreases.
ΔTf =
T°f - Tf
ΔTf =
depression in freezing point
T°f =
freezing point of pure solvent
Tf =
freezing point of solution
 For dilute solution:
For dilute solution:

Δ Tf α
m
Δ Tf =
Kf x m
Kf =
Molal depression constant (Cryoscopic constant). Units: K kg mol¯¹


R = gas constant
M1=
molar mass of solvent
ΔfusH =
enthalpy of fusion

No comments:
Post a Comment